Cellular Respiration Formula Explained

After reviewing the notes about cellular respiration and fermentation the students turn in the notes they have written either online or on paperThe students then take out their Chromebooks and enter the lab where we work on the fermentation demonstration activity.
Cellular respiration formula explained. Glucose oxygen chemical energy carbon dioxide water Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create atp a chemical which the cell uses for energy. A short video covering the topic of cellular respiration including the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration prepared for a year 9 science. Cellular respiration is a process that is undergone in cells to break down molecules and produce ATP.
Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and. Living active or occurring in the absence of free oxygen. Cellular respiration formula explained.
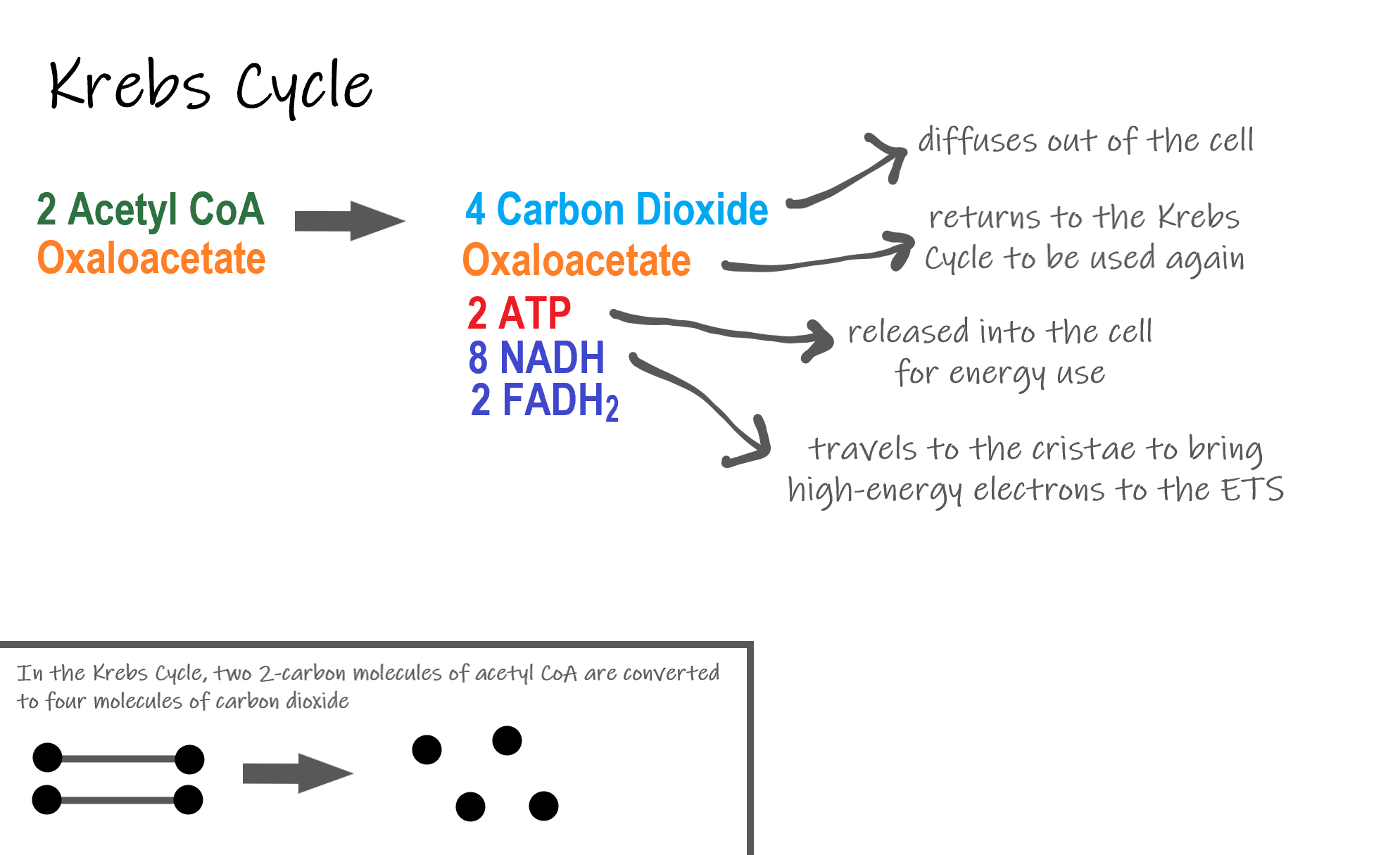
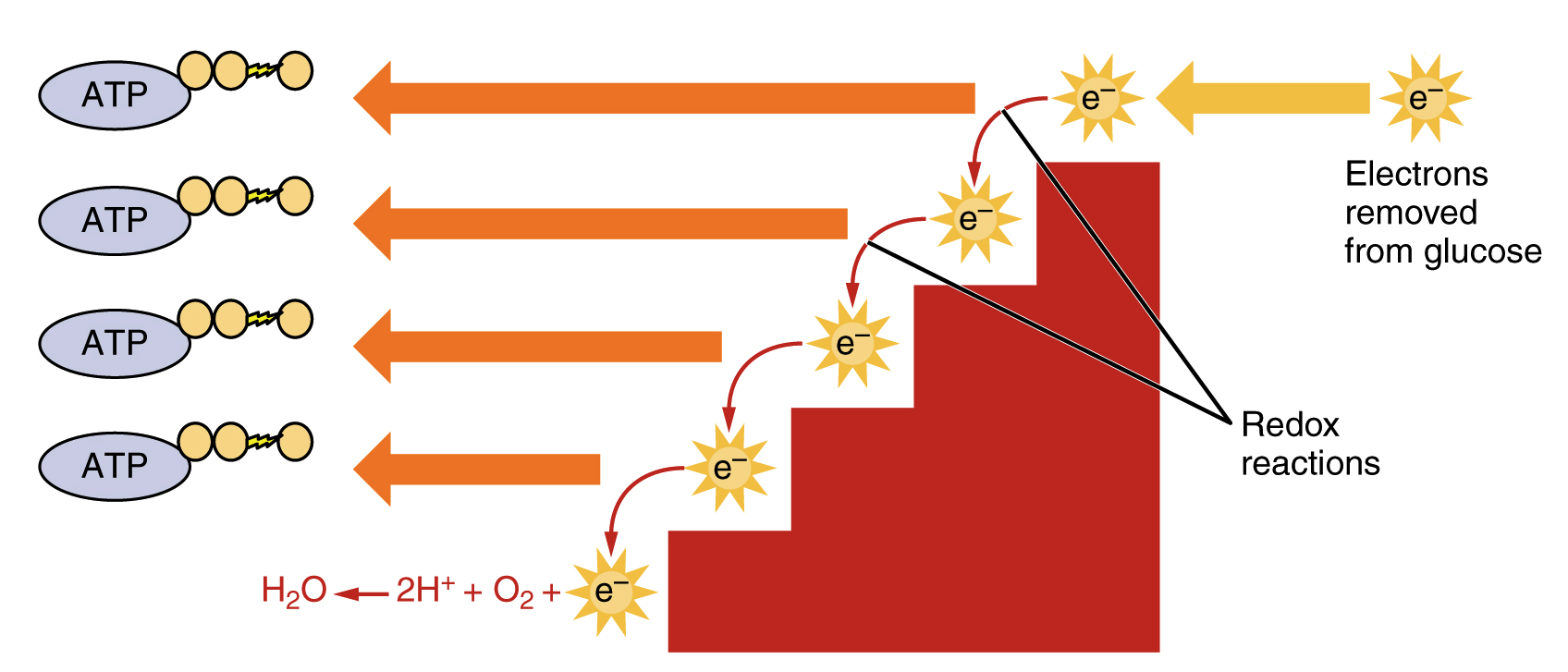
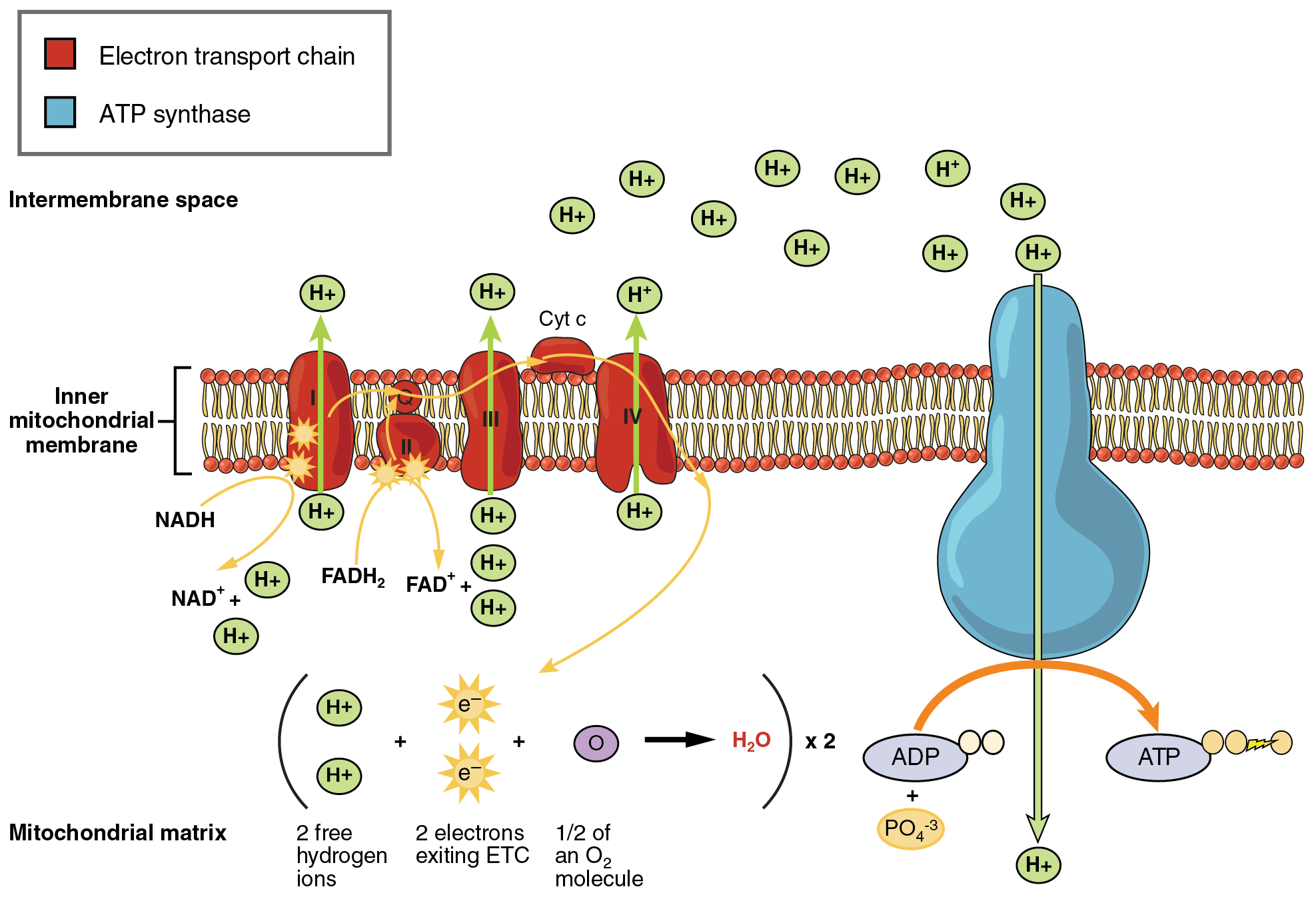
It is important to know that the equation listed above is a summary equation. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in.
The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs where it is exchanged for oxygen. Glucose sugar Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Energy as ATP Aerobic cellular respiration has four stages. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 -- 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O ATP is the complete balanced chemical formula for cellular respiration.
It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. Cellular respiration formula is the collective term for a number of different processes which convert biochemical energy derived from nutrients into a molecule called adenosine triphosphate atp the form of usable chemical energy needed to drive cellular processes. Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
Cellular respiration is a common process that is carried out by many organisms to make and release energy. Process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy. Cellular respiration formula explained.