Cellular Respiration Formula With States

Someone wrote the balanced equation heres the word equation.
Cellular respiration formula with states. Explain why aerobic cellular respiration results in 36 ATPs per glucose in eukaryotic cells and 38 ATPs per glucose in prokaryotic cells. The overall unbalanced chemical equation for cellular respiration is. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
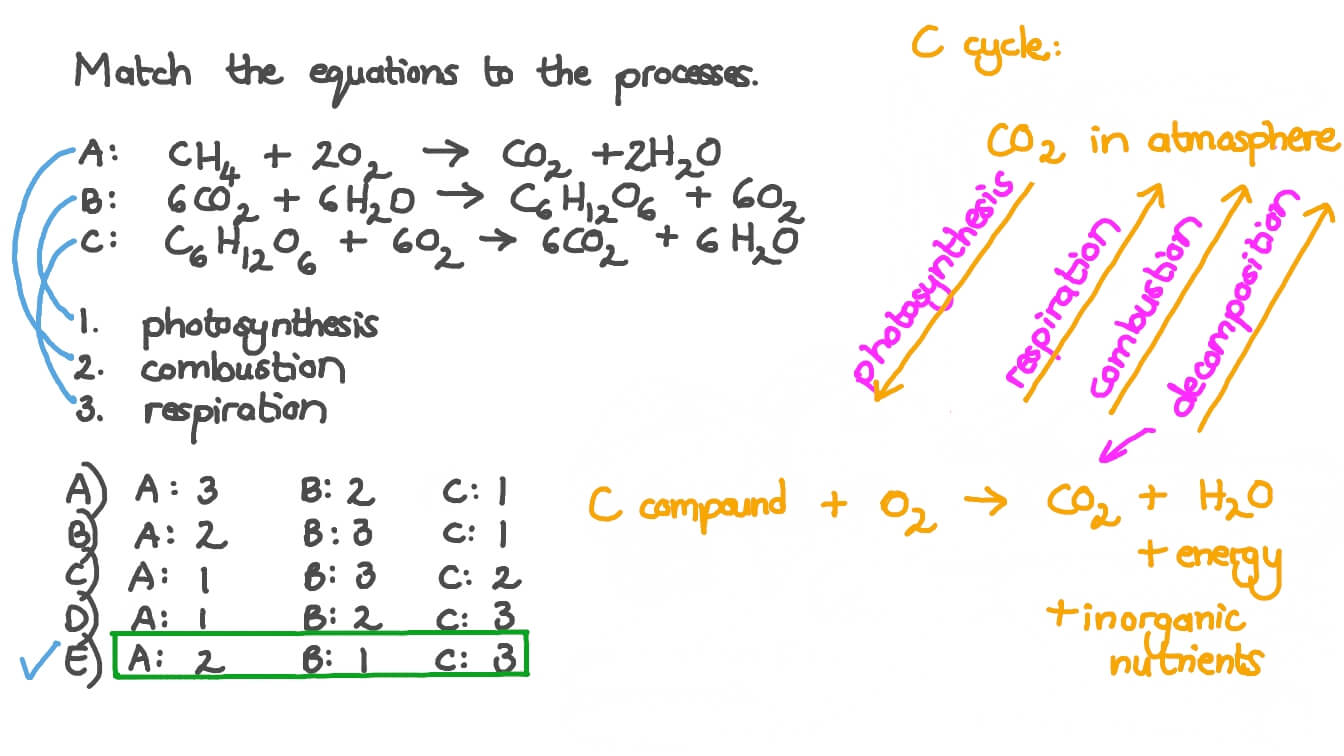
In simplified terms it is. The chemical reaction of cellular Respiration is C6H12O6 6O2 6CO2 6H2O The chemical reaction of photosynthesis is 6CO2 6H2O C6H12O6 6O2 Also Read. Glucose Oxygen Carbon Dioxide water energy Heres an article on it.
The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms. Cellular Respiration as a Series of Reduction-Oxidation Reactions. Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms convert the biochemical energy of nutrients into ATP.
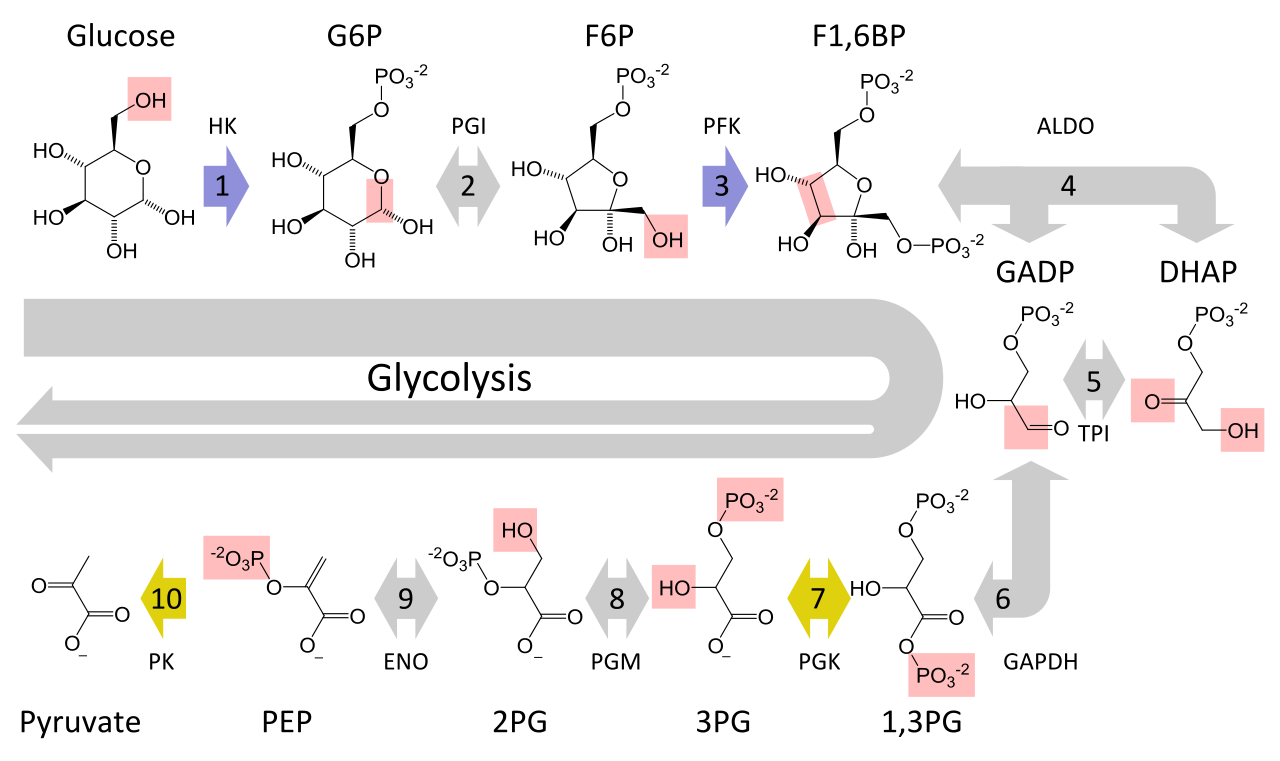
The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and ADP to produce carbon dioxide water and ATP. Anaerobic produces 2 ATP. There are three main stages of cellular respiration.
It is symbolized by the chemical formula of C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2 6CO 2 6H 2 O C 10 H 16 N 5 O 13 P 3 also known as ATP. The word equation for cellular respiration is glucose sugar oxygen carbon dioxide water energy as ATP. It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water.
Cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. A glucose molecule combines with 6 oxygen molecules producing 6 molecules of water 6 molecules of water and ATP. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in particular in molecular oxygen are replaced by stronger bonds in the products.