Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form. A series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance eg.
Related Biology Terms. Refer to the image below for a quick overview of the process taking place during this respiration. In contrast to simple combustion cellular respiration involves the step-wise release of energy in a tightly regulated fashion.
In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP. Cellular respiration biology definition.
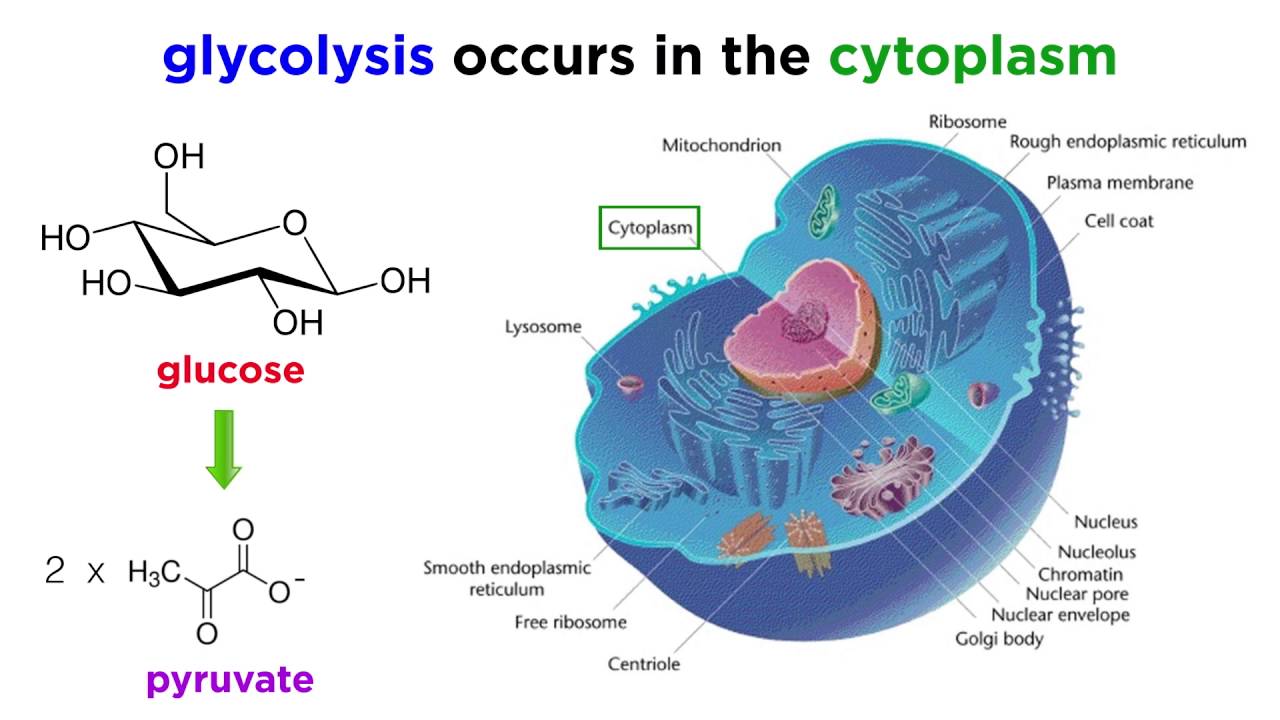
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Other types of organisms such as animals fungi many protozoa and a large. Heterotrophs like humans ingest other living things to obtain glucose.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Cellular respiration Energy from nutrients is converted into ATP. Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n.
Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. Introduction to Cellular Respiration. The cellular context In the diagram at left 1 represents the cell exterior.