Cellular Respiration Takes Place In The Cells Of All Organisms

Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in all living cells to release energy by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate- ATP.
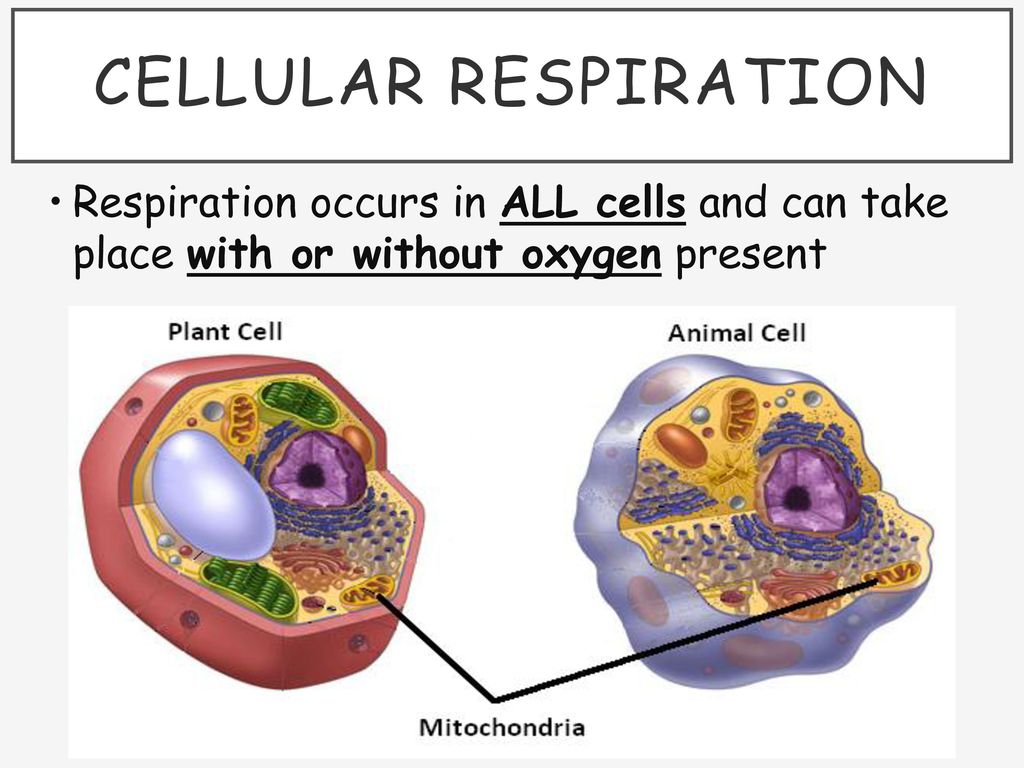
Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms. It is completed in mitochondria. It is completed in mitochondria. Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of animals plants and fungi and also in algae and other protists.
Cellular respiration begins in the cytoplasm of cells. Cellular respiration occurs in the cells of all living things both autotrophs and heterotrophsAll of them burn glucose to form ATP. It occurs in autotrophs such as plants as well as heterotrophs such as animals.
Organisms from all kingdoms of life including bacteria archaea plants protists animals and fungi can use cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. When breakdown of glucose occurs with the use of oxygen it is called aerobic respiration.
It occurs in autotrophs such as plants as well as heterotrophs such as animals. Cellular respiration converts the energy in the bonds of glucose into usable energy for the cell True The usable energy in organisms is usually found in the form of a. Respiration In Organisms Class 7 Science Extra Questions and Answers Very Short Extra Questions and Answers.
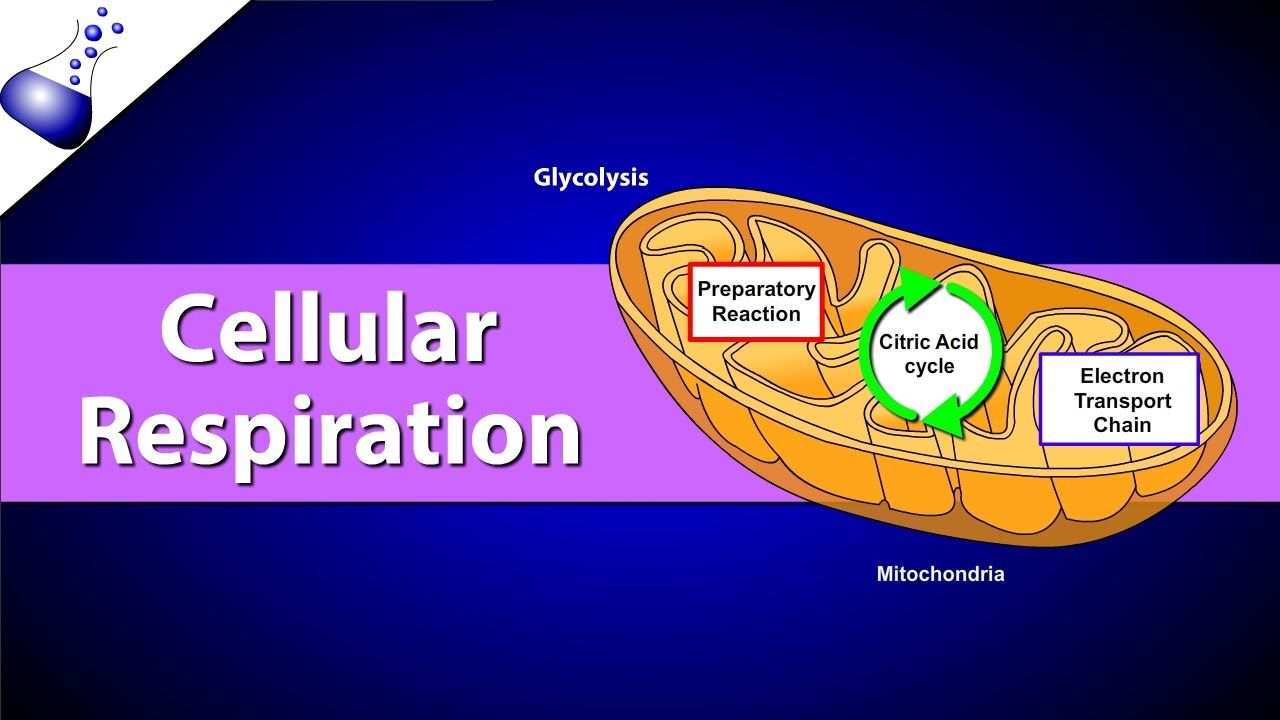
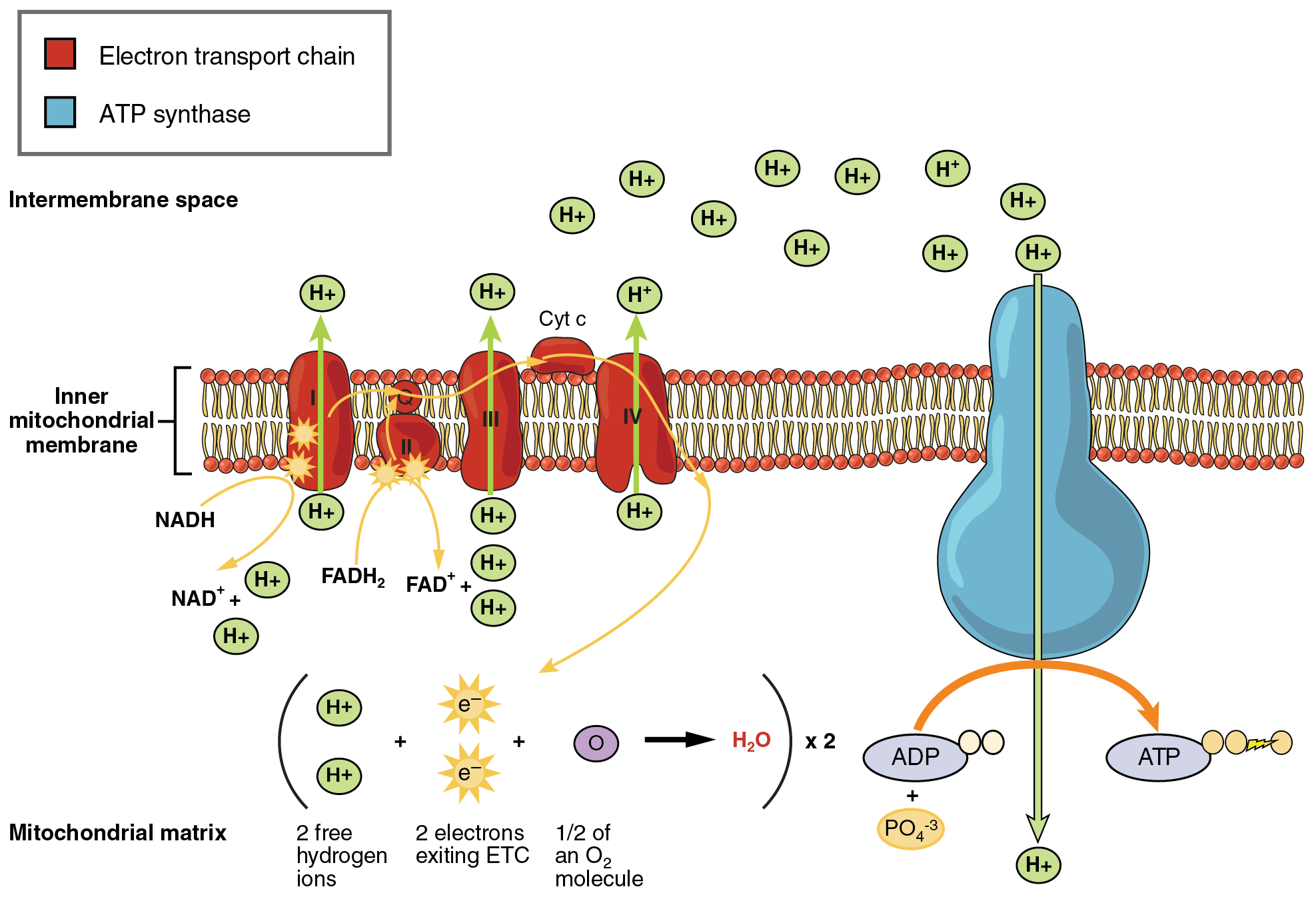
Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down glucose release the stored energy and use the energy to make ATP. The process of breakdown of glucose with the use of oxygen is called aerobic respiration. The overall process of cellular respiration takes place in a number of steps that are specialized for the degradation of specific molecules.
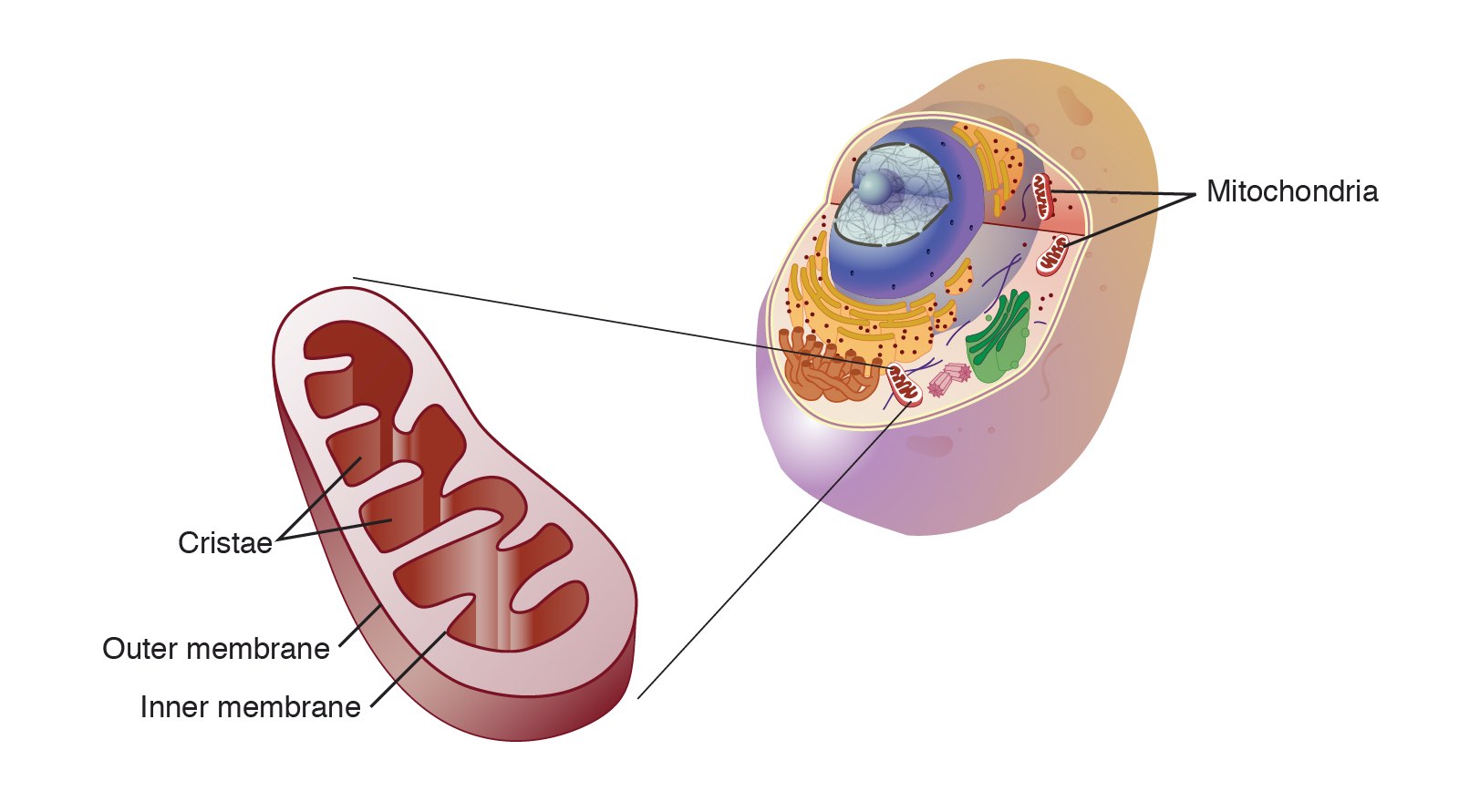
It occurs in autotrophs such as plants as well as heterotrophs such as animals. In its most basic sense cellular respiration is a number of different metabolic processes and reactions that happen in cells. The mitochondrion is a membrane enclosed organelle in the cytoplasm.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)

/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)