Cellular Respiration Takes Place Inside The

This process produces energy within the cell.
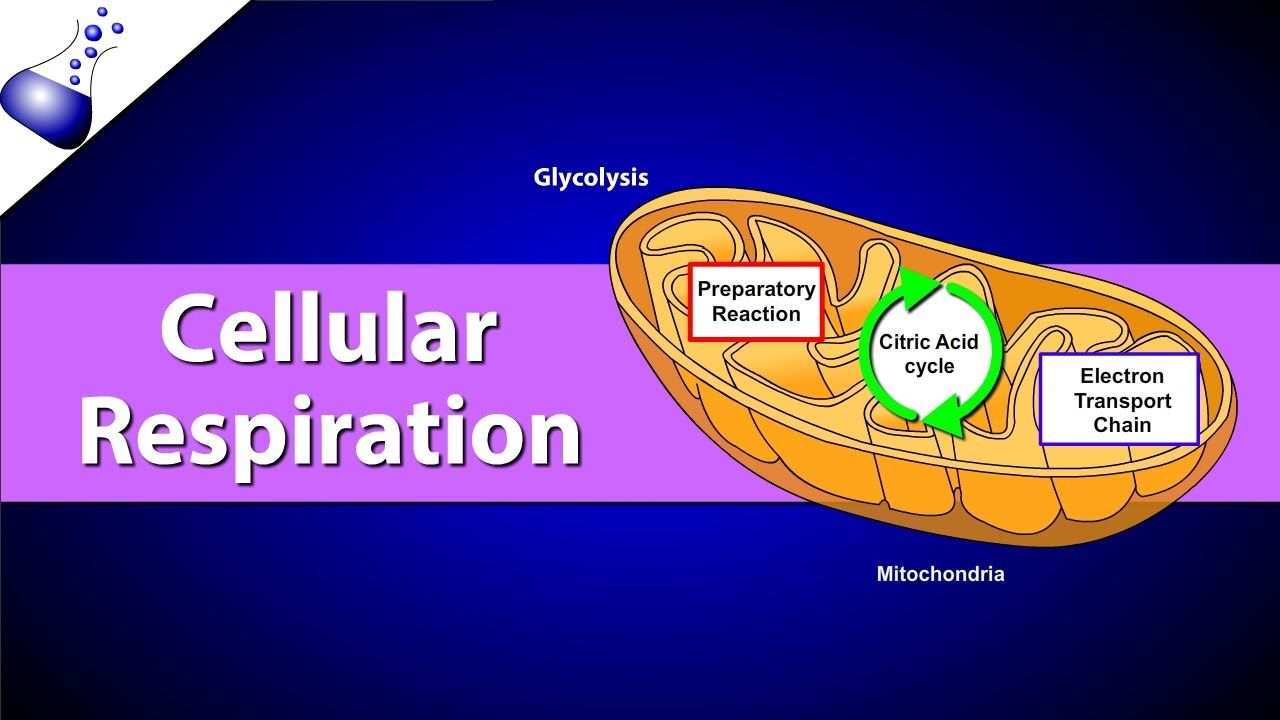
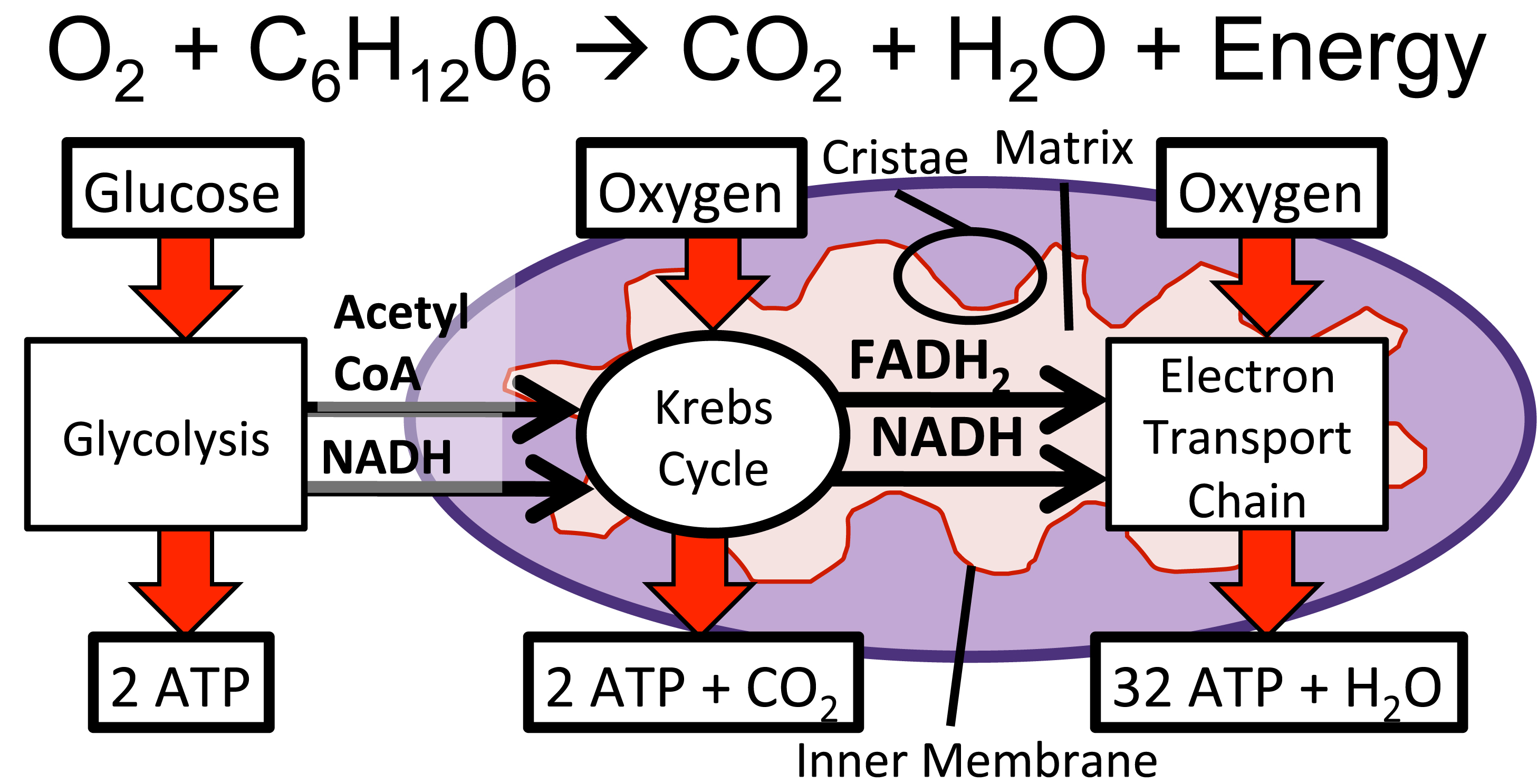
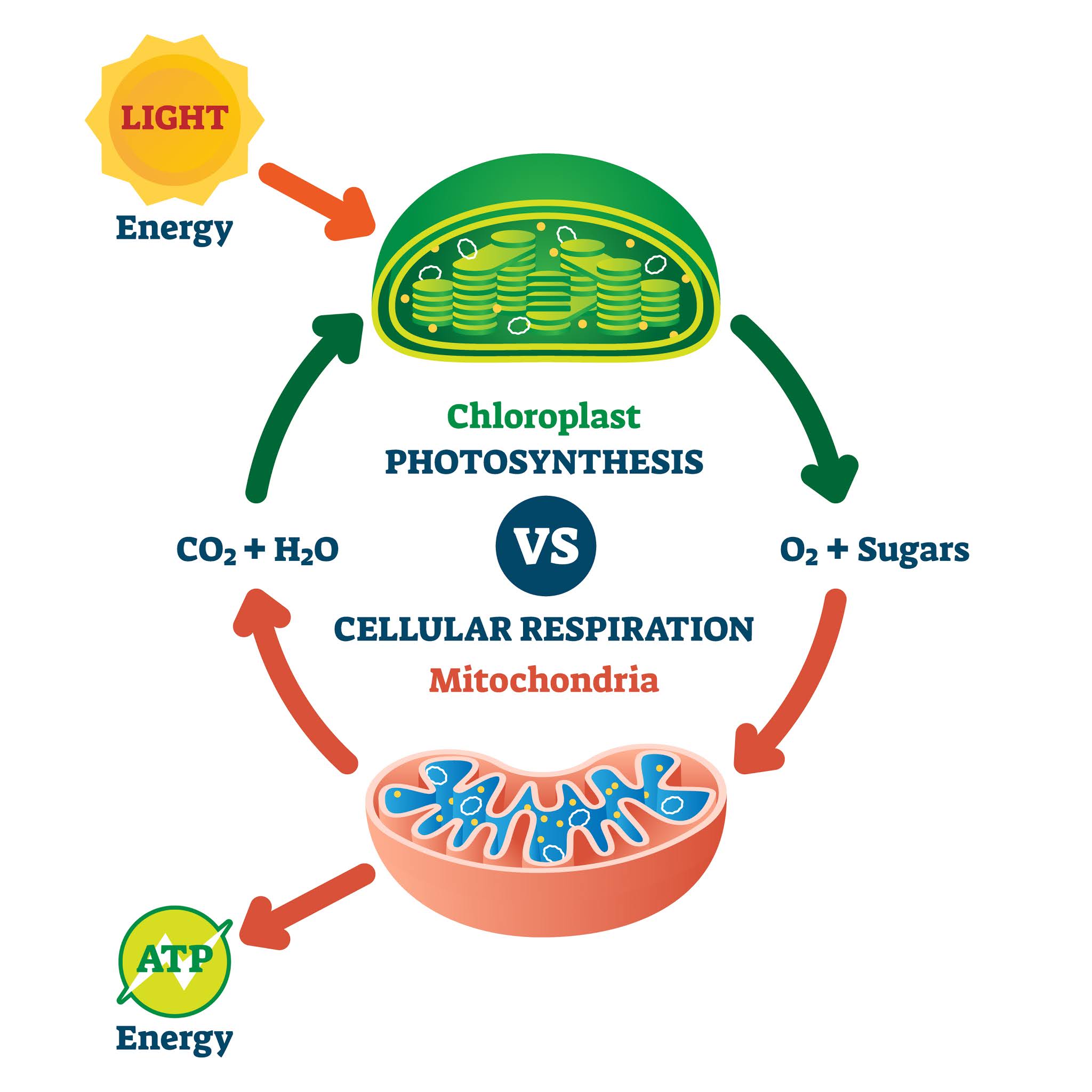
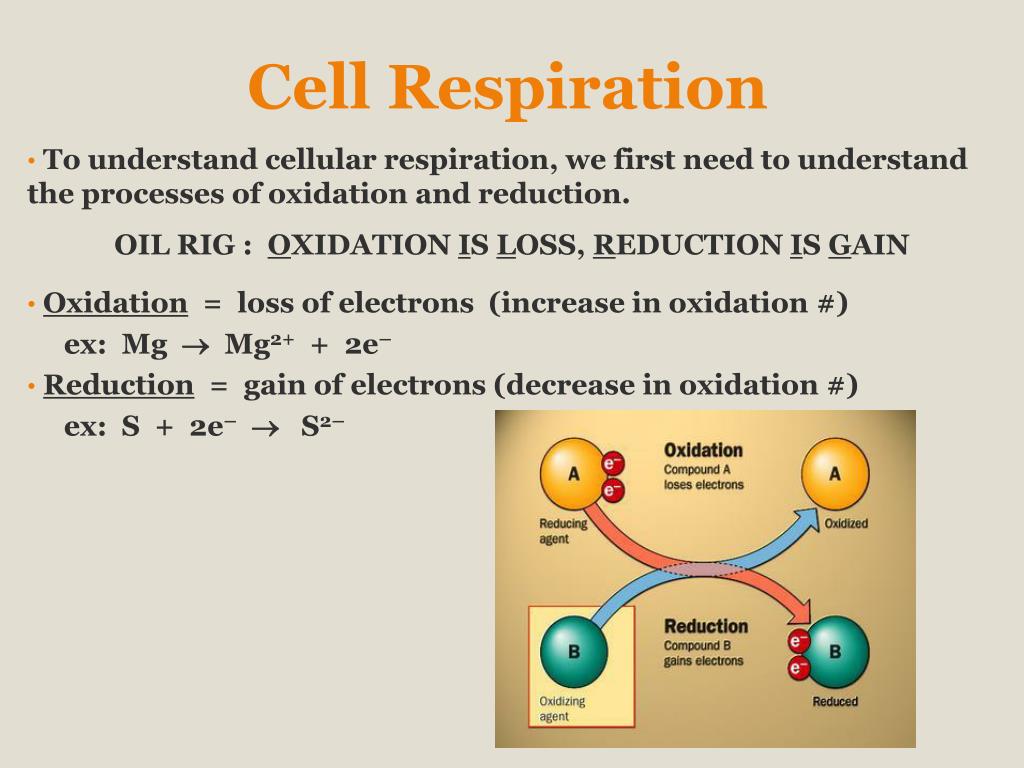
Cellular respiration takes place inside the. Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate ATP. According to Hartnell College cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm of cells and inside the mitochondria.
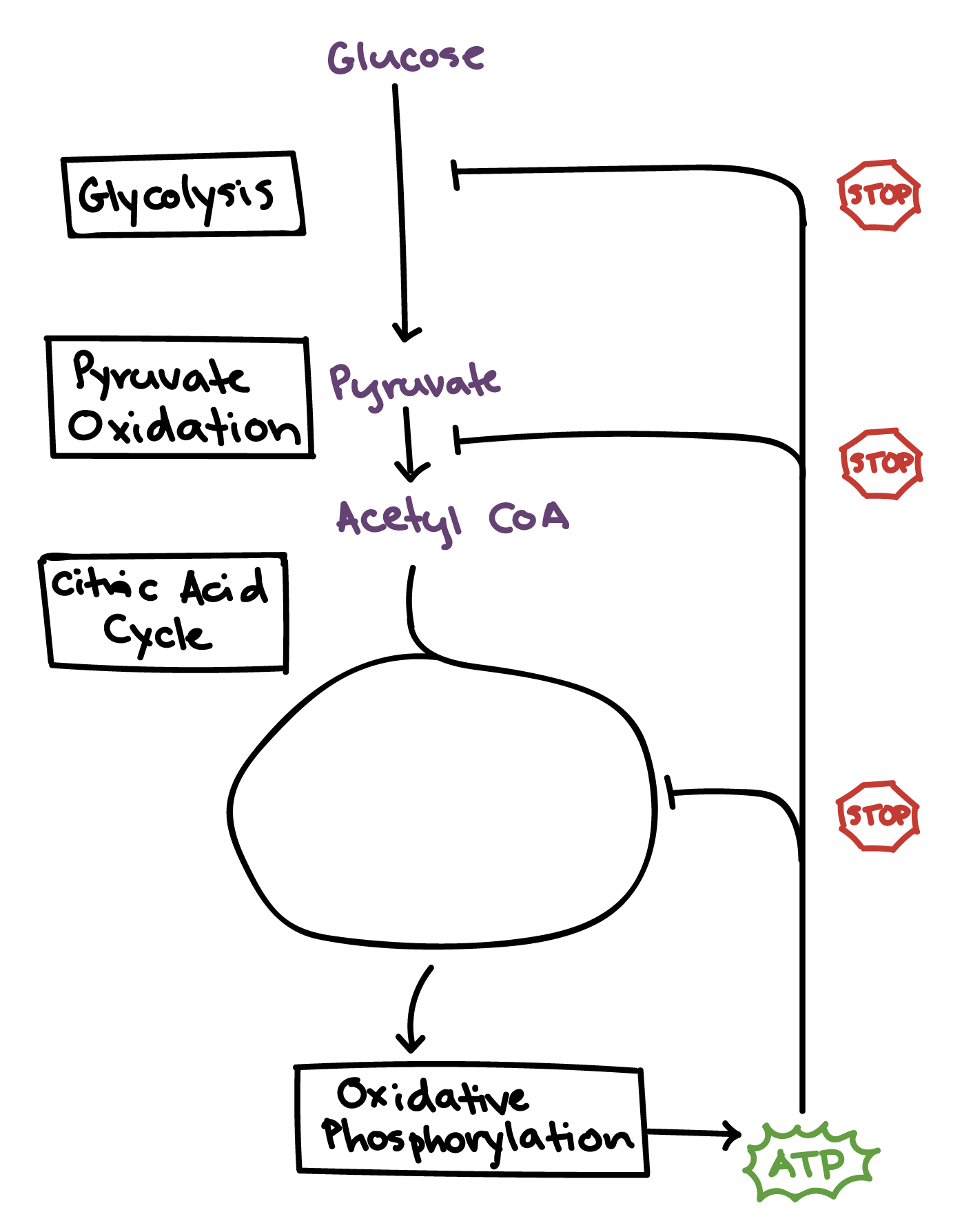
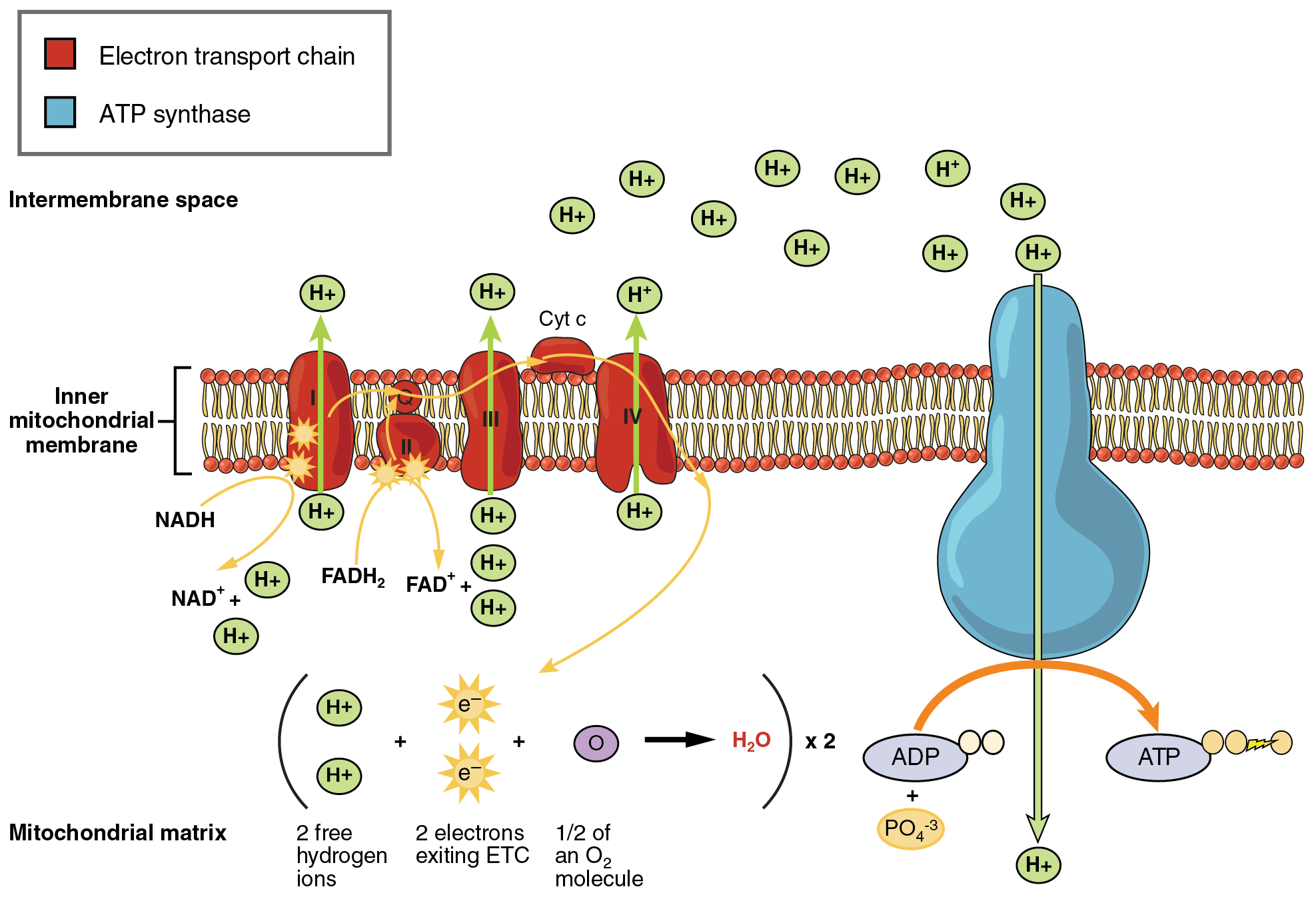
Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and electron transportoxidative phosphorylation. Two steps of Respiration that take place in the mitochondria of all cells. Have a look at the.
The first half is known as the energy requiring steps. Specifically cellular respiration happens inside the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. Powerhouse of the cell organelle that is the site of ATP energy production.
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria of plant cells. There are two halves of glycolysis with five steps in each half. Membrane vesicles containing an internal sodium chloride nacl concentration of 014 m are placed into separate beakers each containing a different solution.
The energy currency of these cells is ATP and one way to view the outcome of cellular respiration is as a production process for ATP. Cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. Cellular Respiration is the process that takes place in cells to convert food into energy.
More emphasis here will be placed on eukaryotic cells where the mitochondria are the site of most of the reactions. The first beaker contains 014 m sucrose while the second beaker contains 014 m calcium chloride cacl2. Cellular respiration is a critical function by which cells release energy for various cellular activities like locomotion biosynthesis and even the transportation of molecules between membranes.