Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

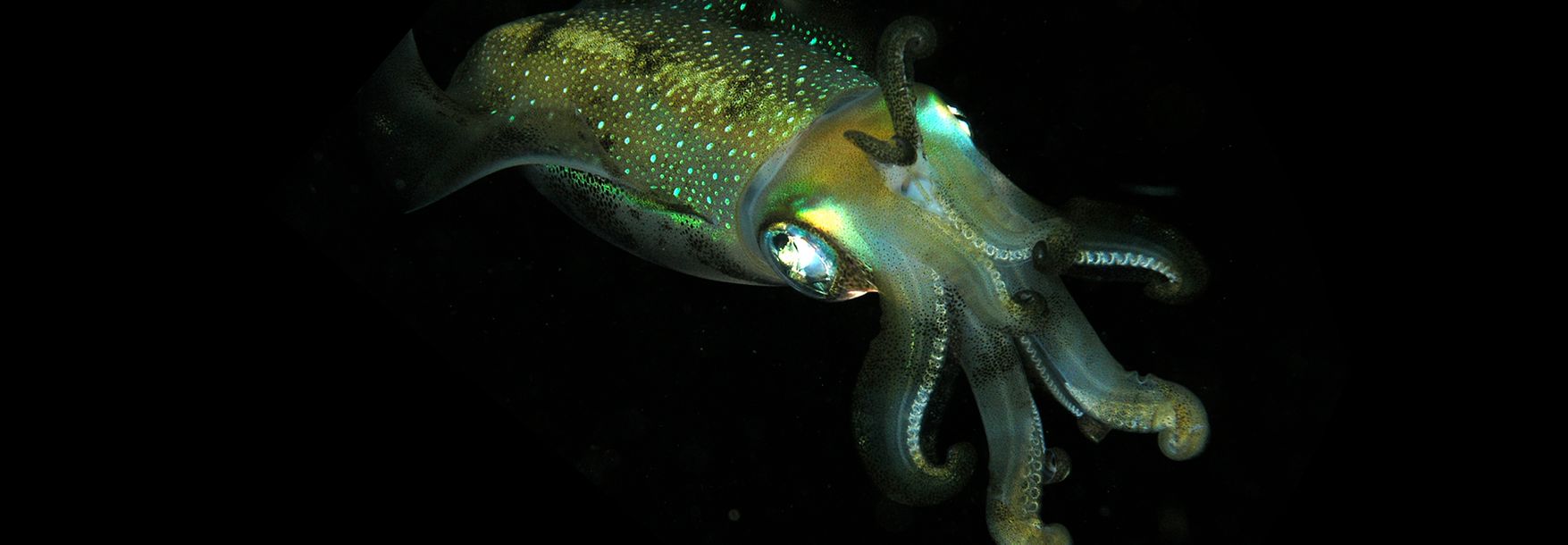
They have streamlined bodies to help them swim fast and gills that suck the oxygen out of the water so they can breathe.
Deep ocean animals adaptations. Coastal plants need special adaptations to survive. The intertidal zone the pelagic zone and the abyss. Childress T he deep ocean is unlike terrestrial and shallow en- vironments in many ways but two of the most im- portant are its vast scale as a habi- tat and the pervasiveness of con- ditions throughout it.
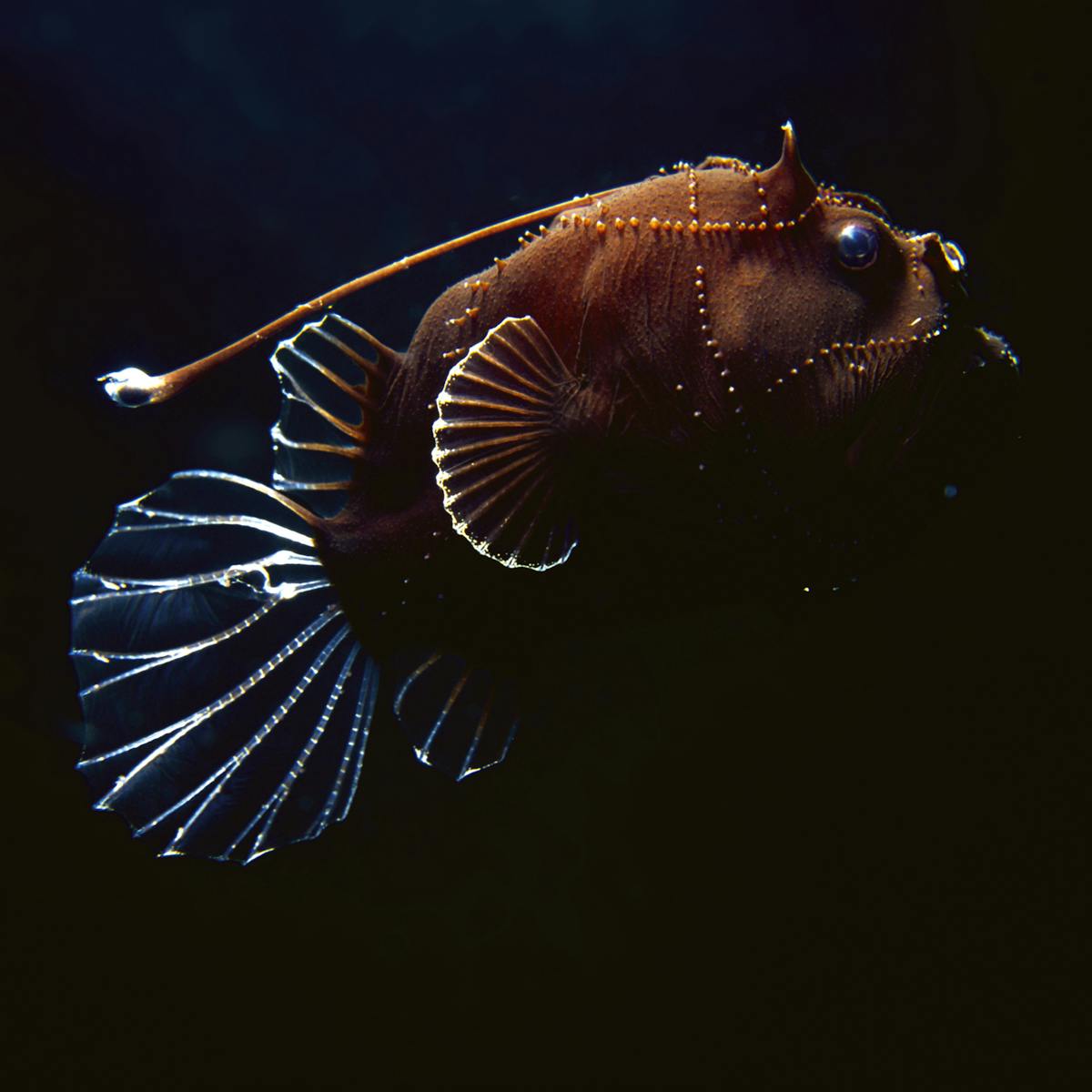
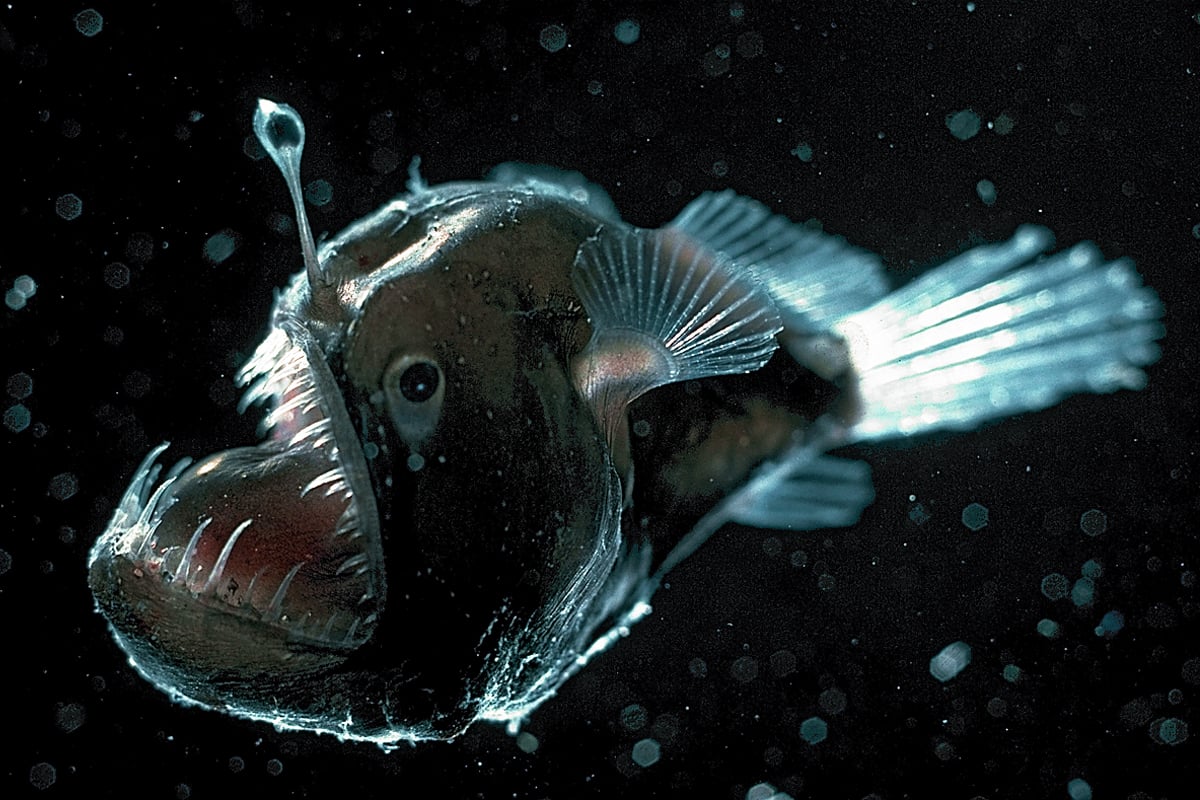
In some other deep-sea fishes eyes are very small as they are of little apparent use and still others are without eyes. Fish Biologist Kate Bemis Illustrator Rachel Keeffe and Ocean Educator Lara Noren. Animals adapt to their environments to help them survive.
Dissolved H2S emerging from. Water depth temperature and the presence or absence of light are some of the conditions that differ in these habitats. The abilities of deep-sea animals to tolerate the pressure and temperature conditions of deep-sea habitats are due to pervasive adaptations at the biochemical level.
Contains a chart for students to label the different zones of the ocean as well as a chart to keep track of different animalcreature adaptations in different zones. The dense ocean water is filled with tiny floating organisms. Enzymes exhibit reduced perturbation of function by pressure membranes have fluidities adapted to deep-sea pressures and temperatures and proteins show.
Some of the most amazing adaptations are from ocean animals like sharks jellies starfish stingrays and dolphins. Seep communities are more dispersed in areas where hydrocarbons particularly methane or other natural gases are percolating up through deep-sea sediments. 8 12 x 11 blank paper pencil colored pencils ruler or straight edge.
Have students identify animal adaptations in. Some of the most amazing adaptations are from ocean animals like sharks jellies starfish stingrays and dolphins. Animals adapt to their environments to help them survive.