Transgenic Animals Definition Biology

Sheep goats pigs cows rabbits rats mice fish insects parasites and even humans have previously been used in this modification process.
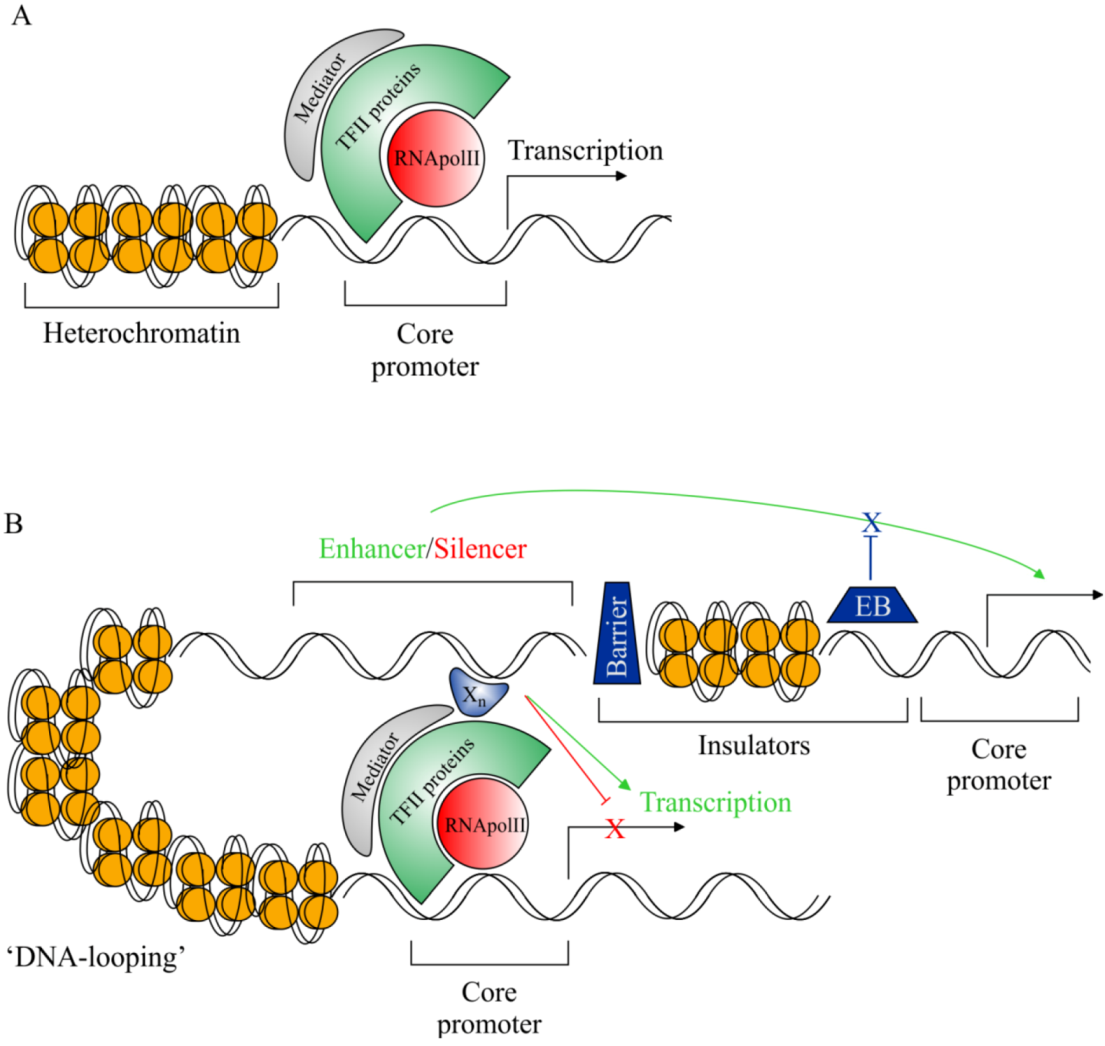
Transgenic animals definition biology. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. Transgenic means that one or more DNA sequences from another species have been introduced by artificial means. Transgenic animals - definition.
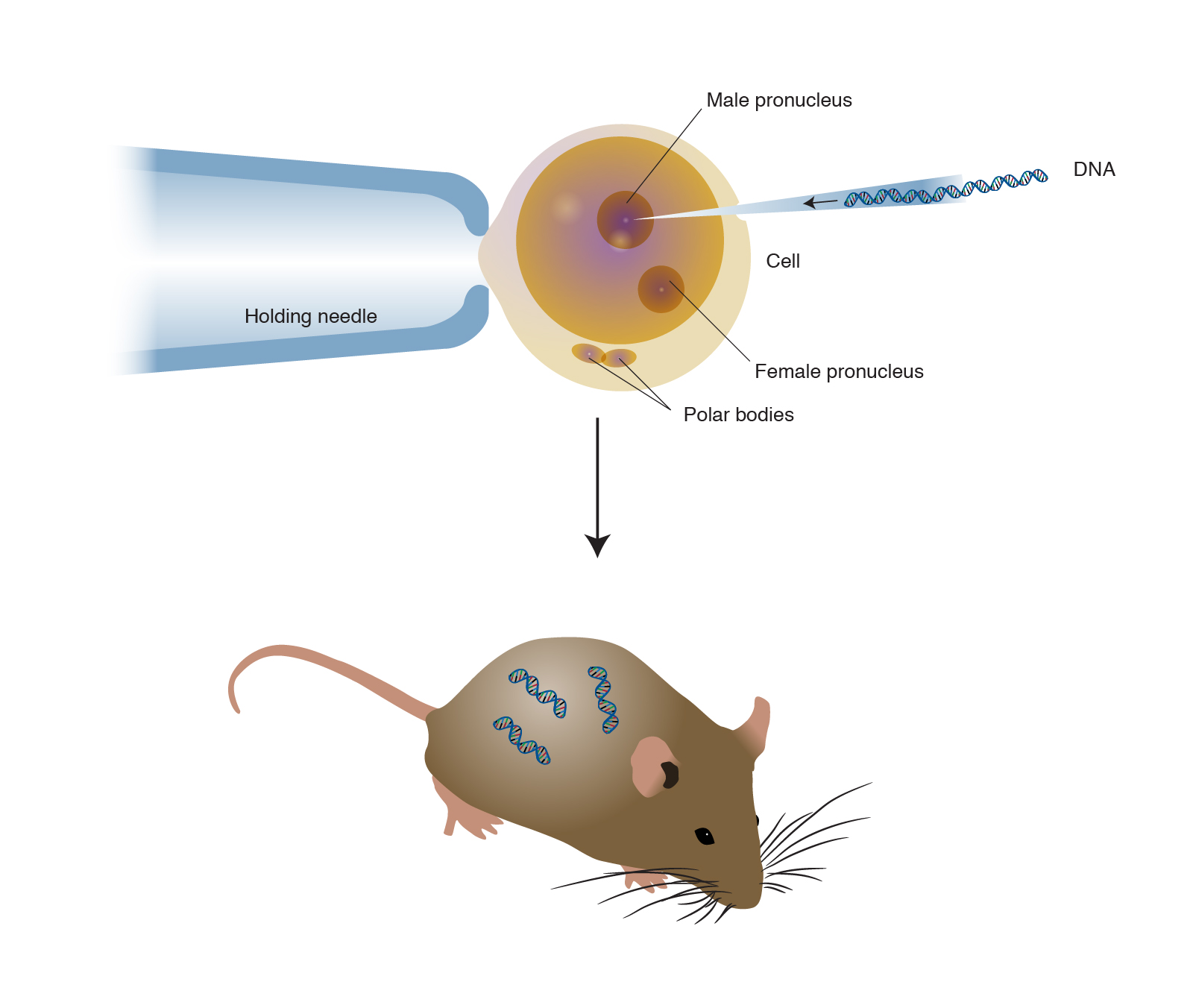
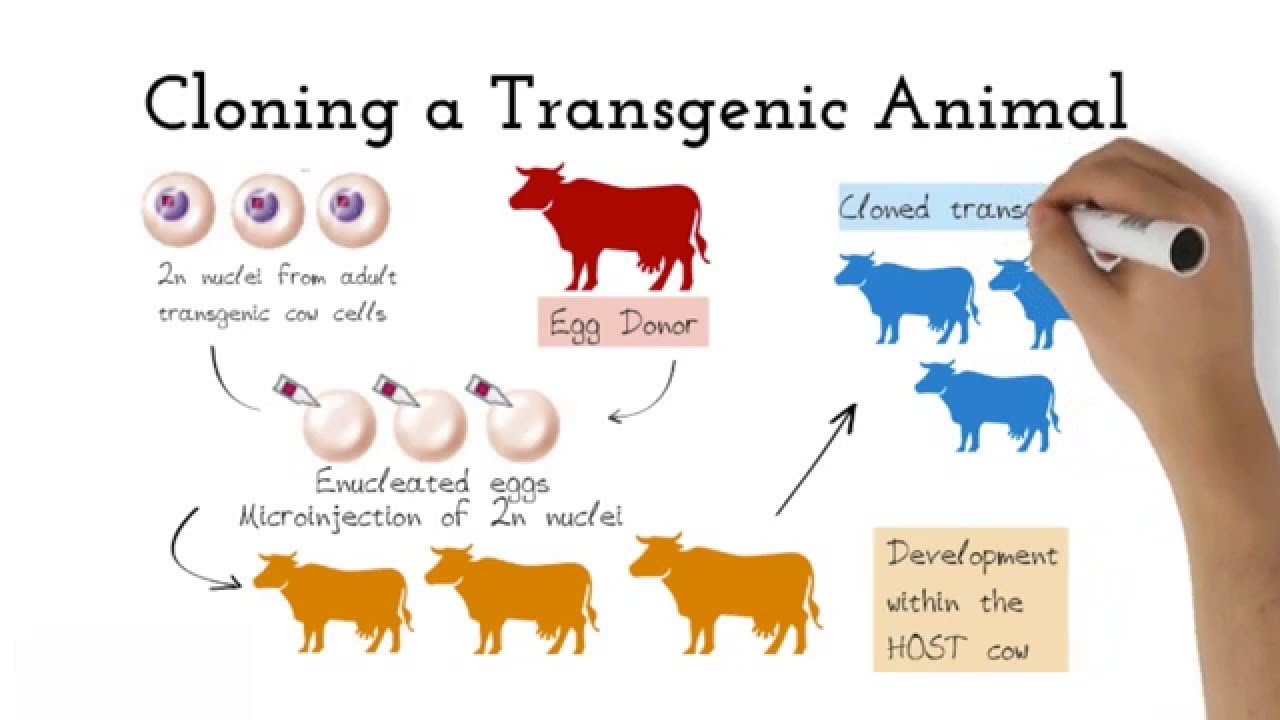
Transgenic animals are those that have been genetically modified. Animals transgenic animals or the offspring of such animals into which cloned genetic material has been experimentally transferred by microinjection of foreign dna either directly or into embryos or differentiated cell types. Arise from pluripotent stem cells.
Full article Transgenic Animals The. In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it. These transgenic models are used in research for the development of medicines.
In addition to the gene. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been altered by the transfer of a gene or genes from another species or breed.
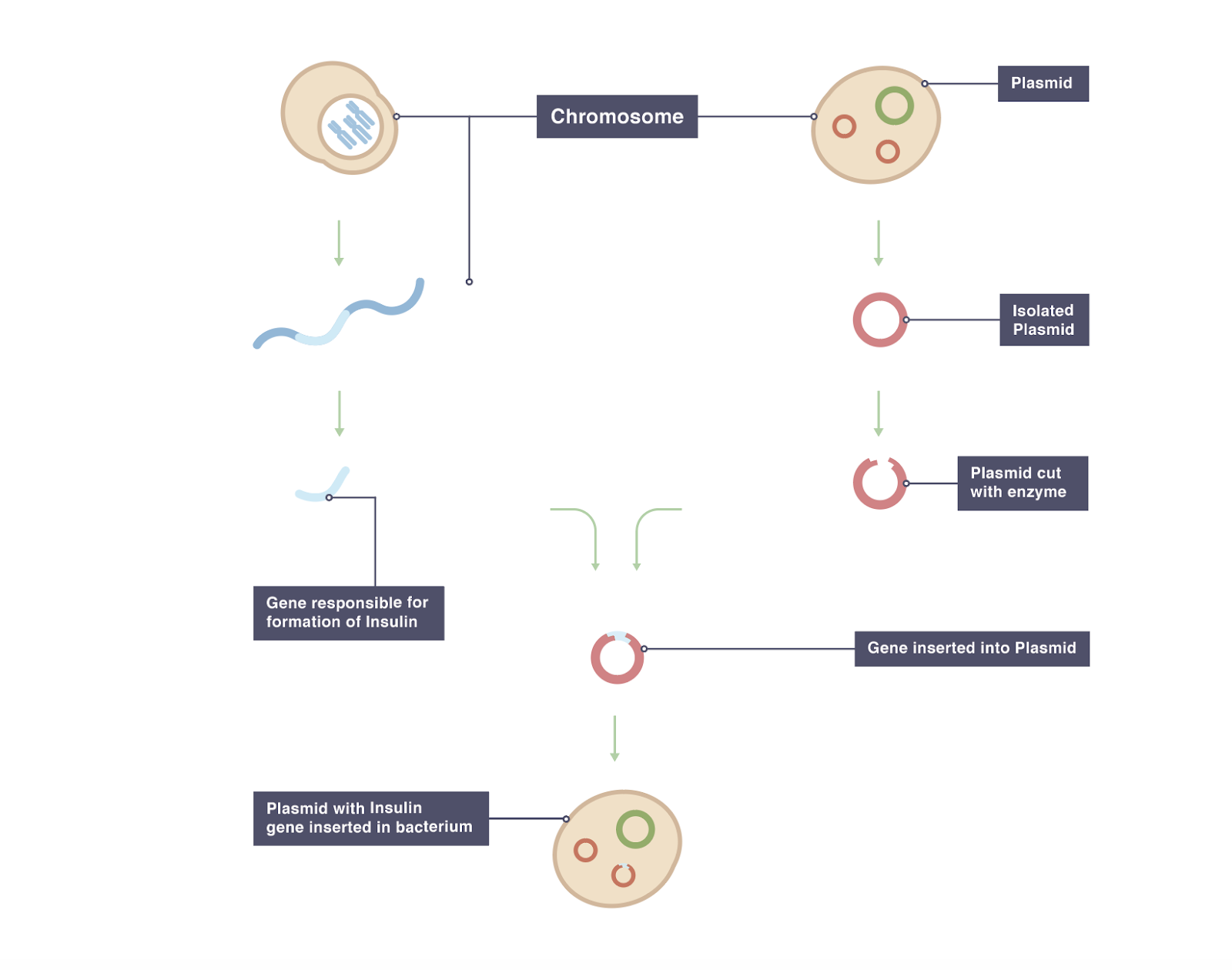
Theoretically all living beings can be genetically manipulated. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. The term transgenic animal refers to an animal in which there has been a deliberate modification of the genome - the material responsible for inherited characteristics - in contrast to spontaneous mutation FELASA September 1992 revised February 1995.
The foreign DNA or transgene that is transferred to the recipient can be from other individuals of the same species or even from unrelated species. Recombinant DNA methodology is used to construct the gene that is intended to express desirable qualities during the growth and development of the recipient animal. Transgenesis is the process by which mixing up of genes takes place.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)