Transgenic Plants And Animals Wikipedia
It was in 1995-96.
Transgenic plants and animals wikipedia. Usually ear tissue and blood are screened by polymerase chain reaction andor Southern analysis for the. For this reason the desired genes are cloned and expressed in animals such as sheep goats chickens and mice. A transgenic plant contains a gene or genes that have been artificially inserted.
Transgenic models are more precise in comparison to traditional animal models for example the oncomouse with its increased susceptibility to tumor development enables results for carcinogenicity studies to be obtained within a shorter time-frame thus reducing the course of tumor development in experimentally affected animals. A foreign gene will be inserted into a plant of a different species or kingdom. The cell uses CO 2 water minerals and sun light to synthesise thousands of valuable and complex products which are the basis of animals life.
The very purpose of production of transgenic plants is for their commercial importance with high productivity. Transgenic Plants as Bioreactor Molecular Farming. TRANSGENIC PLANTS- The plant whose genome is altered by adding one or more transgenes are known as transgenic plants.
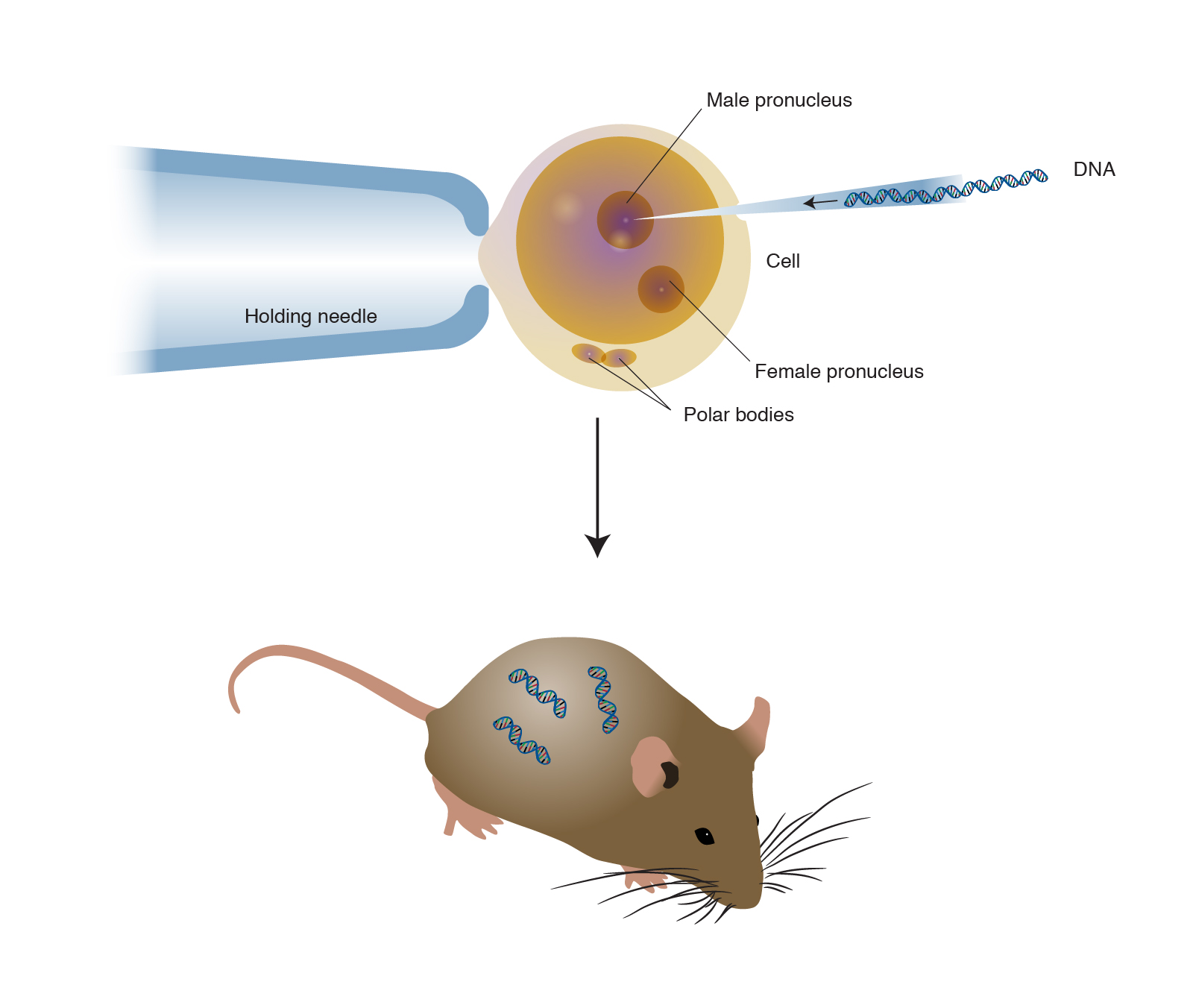
Transgenic plants are the ones whose DNA is modified using genetic engineering techniques. The aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome.
Plant cells act as the Natures cheapest factory. The foreign gene that is introduced is known as the transgene and the animal whose genome is altered is known as transgenic. Transgenesis is the phenomenon in which a foreign gene with desired characteristics is introduced into the genome of the target animal.
Transgenic plants can produce a variety of proteins used in diagnostics for detecting and curing human and animal diseases in large scale with low cost. Transgenic animals for the production of therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are produced by transferring fertilized transgene-carrying embryos to recipient animals. Although several recombinant proteins used in medicine are successfully produced in bacteria some proteins require a eukaryotic animal host for proper processing.